Osteochondrosis is one of the most common diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which manifests itself as a result of a complex of certain dystrophic changes in the vertebra's cartilage, during this pathological process, the spinal discs are frequently affected. The structures, which are the intervertebral cartilage discs, provide flexibility and also allow the human spine to move, that is, they provide movement.
With osteochondrosis, several processes occur that cause degeneration of the vertebral discs, with which they begin to lose elasticity and reduce the degree of flexibility, and at this moment the disc itself becomes quite flat. The distance between the two discs decreases, while compressing nerve endings and blood vessels and causing severe pain. The compression site of the nerve node begins to swell, which leads to increased pain and even greater infringement.
During the development of osteochondrosis, muscle structures and most of the body's organs are often involved in this pathological process. This is due to the fact that during the maximum infraction of the neurovascular bundle, blood circulation and motility of muscles and organs are disturbed. For example, the most common osteochondrosis is cervical osteochondrosis, which is accompanied by pain in the back of the head, nausea, dizziness, visual impairment and, often, tinnitus. This disease has become quite "young": a century ago, osteochondrosis was a disease of people of gerontological age and today young people are also susceptible to it.

The most vulnerable category of people are those who have severely compromised metabolism and hormone levels in the body, as well as people who have disorders of a vascular-venous nature. This is due to the fact that these diseases cause disruption of disk oxygenation. If qualified, timely measures are not taken to heal, so the edges of the affected intervertebral disc, which is compacted, will project anatomically beyond the boundaries of the spine, thereby destroying the neurovascular bundles.
Because of this, the patient is at risk of having a herniated disc. The main and significant cause of osteochondrosis is the uneven distribution of the load in the spine, which leads to the fact that the cartilaginous structure changes in points with excessive pressure. The nature of this disease depends on the stage and the level of damage to the affected discs. Intervertebral discs change with age, as does our hair. Serious injuries or fractures of the spine can affect its functioning. Casual clothing and certain types of vibration can also accelerate the rate of spinal degeneration. In addition, the evidence suggests that smoking increases the rate of spinal degeneration. Scientists have also discovered a link between family members, highlighting the role of genetics in how quickly changes occur.
The disease can also be triggered by a variety of factors:
- injuries, bruises;
- dystrophy of the spinal muscles;
- tilt and curvature of the spine;
- lifting weights;
- prolonged stay in one position;
- metabolic disease;
- lack of trace elements and vitamins - manganese, magnesium, zinc and vitamins D and F;
- hereditary predisposition;
- physical overload;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- radiation background;
- Cold burn;
- congenital dystrophies;
- asymmetric work of the spinal muscles;
- stress, depression.
These causes of osteochondrosis are just assumptions of scientists, direct factors that cause the disease, which science has not yet discovered, and we are only talking about risk factors.
First perioddevelopment - characterized by the early unfolding of the intradiscal pulpous nucleus (pulpous nucleus of the eccentric intervertebral disc, located close to the dorsal part of the vertebra).
Second periodcharacterized by the appearance of instability of the spinal segment. Pathological substrates are represented by the fibrous nucleus of the affected disk with degenerative processes of take-off and fragmentation of the posterior longitudinal ligament, developing pathological movements between the vertebrae.
Third periodthe development of the disease - total damage to the intervertebral disc, with the appearance of a "herniated disc" - displacement and exit of fragments of the pulpous nucleus out of the intervertebral space.
If the disease has reached the third stage, the destruction process is already irreversible and can lead to a profound deficiency.
Types of osteochondrosis
The evolution of osteochondrosis is slow, with exacerbations caused by spinal injuries, exercise, carrying weights, etc. The clinic depends on the location of the lesion.
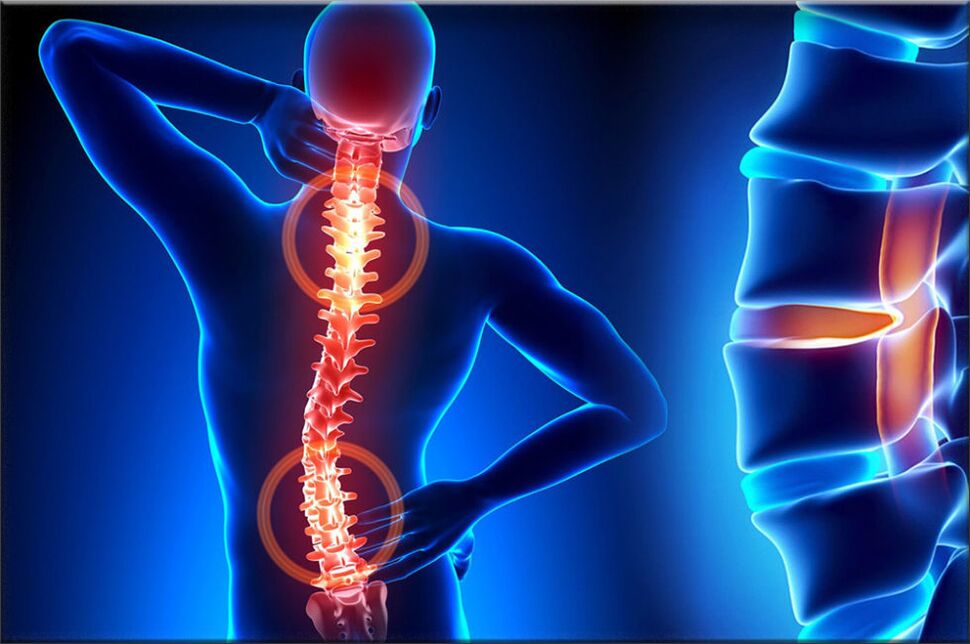
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spineit presents local and remote symptoms in advanced ways - with strong root control, that is, it contributes to the development of intense root pain. Symptoms of osteochondrosis in the cervical spine are accompanied by varying degrees of dysfunction, sometimes manifested by a sudden limitation of cervical spine mobility and functional blocks. Headaches can be severe and paroxysmal in nature, radiating to the interscapular region or shoulder region. In the acute period, patients are diagnosed with bouts of pain in the neck, which prevent and restrict the movements of the head and neck. In addition to intense discomfort, the painful syndrome can be accompanied by dizziness, insomnia, pain, loss of appetite, depression, diseases of the eyes and pharynx.
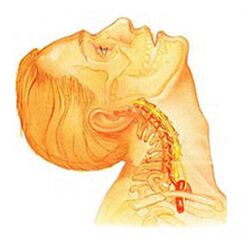
Thoracic osteochondrosis. . . The clinical manifestations are due to local lesions and processes of destruction of the root structure of the nerve. Thoracic osteochondrosis has a pronounced pain syndrome, which can be chronic or acute in back pain with chest discomfort and limited muscle contracture, until atrophy of the right verbal muscle. Chest pain can manifest as diffuse, intercostal and neuralgic. Palpation increases the axial rotation of the vertebral body. The disorders correspond to the level of root irritation from Thl1 to Thl2 and can manifest as angina pectoris, reflected in liver and gastrointestinal tract disorders. Often, disorders of the genitourinary system and genital area occur. Patients note that sensory disturbances, such as paraesthesias, superficial and deep sensitivity, are significantly reduced.
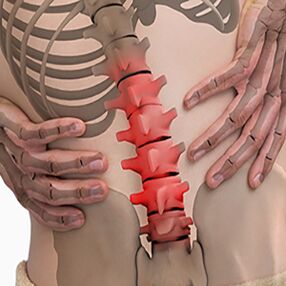
Lumbar osteochondrosis. . . It is characterized by abdominal reflexes and dysfunction of the lower extremities. During the development of neurological disorders, muscle weakness in the legs and dysfunctions of Organs pelvic organs may occur. Osteochondrosis is characterized by the assessment of damage to the sitting process. The more advanced the stage of development of the lesion in the lumbar vertebrae, the shorter the period of time that the patient can sit. The lumbar forms are characterized by acute and chronic low back pain, spasm of the paravertebral muscles and secondary myofascial syndrome. The pain radiates to the buttocks and posterior ilium.
Depending on the location of the pathological process of osteochondrosis, the disease can lead the patient to a violation of superficial sensitivity (tactile, thermal). Also characteristic are changes in reflexes (for example, the Achilles reflex is absent), muscle loss, muscle tone disorders, autonomic disorders (pallor, redness of the skin, trophic changes in the nails, cutaneous hypothermia in the distal extremities), sphincter dysfunctionsand sexual dysfunctions.
Clinical condition
Diagnosisbegins with a complete history and physical examination. The doctor asks questions about the symptoms, how the disease interferes with the patient's daily activities. In addition, the specialist is interested in identifying positions and activities that emphasize or reduce the level of pain.
The doctor then examines the patient, checking the position and range of motion of the spine, thereby determining which movements are causing the pain. Skin sensitivity, muscle strength and reflexes are tested equally. Based on your medical history and physical examination, your doctor determines which techniques will help you.
Radiography rarely helps with diagnosis; no more than 30% of radiographic images show abnormalities in the early stages of disease development.
However, if the symptoms are severe and the disease is already in its second or third stage, defects in one or more intervertebral discs can be seen in the image. They can be penetrated by osteophytes between the vertebrae and the joints.
If additional information is needed, MRI is prescribed. Magnetic resonance imaging is used to visualize the soft tissues of the body. This is useful if the tissue core absorbs water or if there are cracks inside the disc. An MRI can show problems in other soft tissues, such as spinal nerves.
Discography can assist in diagnosis. This test is performed with a contrast agent, which is injected into one or more disks, respectively. The subsequent visualization on the radiograph provides useful information about the condition of the discs.
Treatment of osteochondrosis, depending on the varieties
Non-surgical treatment of osteochondrosis
Whenever possible, doctors prefer non-surgical treatment. The most important thing in non-surgical treatment is to relieve pain and other discomfort so that the patient can return to a comfortable standard of living as much as possible.
Doctors rarely prescribe bed rest for patients with osteochondrosis problems. Patients are encouraged to live in natural mobility when pain is not a concern. If the symptoms are severe, several days of bed rest may be prescribed.
When the spine is displaced, an elastic band is sometimes prescribed, which is not used for more than 2 to 4 days to prevent atrophy of the back muscles.
Osteopathy sessions provide great relief from osteochondrosis.Osteopath doctornot only does it diagnose a problem area, but it also relieves pain in 1-2 doses, relieves the general condition of the body and "tensions" visceral organs.
Patients can receive prescription drugs to control symptoms and resume normal activities for a long time. If symptoms continue to restrict the patient's activities, a conventional doctor may suggest an epidural injection of steroids.
Steroids are powerful anti-inflammatories, helping to relieve pain and inflammation. Injections of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are injected into the space around the spinal roots of the spine. This place is called the epidural space. Some doctors inject the steroid alone. However, it is most often combined with other drugs. Basically, steroids are prescribed only when other drugs are ineffective, but osteopathy almost always helps.
In addition, patients often work with physical therapists. After assessing the patient's condition, the therapist prescribes exercises to reduce symptoms. The exercise program aims to improve flexibility and is useful for training abdominal and back muscles to allow movement with minimal pain.
Surgery
People with osteochondrosis problems generally do not require surgical treatment. In fact, only 1-3% are operable. Surgeons prescribe non-surgical treatment, namely craniosacral osteopathy, as rehabilitation therapy, for at least 3 months before considering surgery. If after 3 months of non-surgical treatment there are no results, then there are reasons to indicate a surgical procedure.
Basic surgical procedures
Discectomy
The procedure aims at the partial or total removal of the disc from the lumbar region. Surgeons usually perform the operation through an incision in the lower back. Before removing a herniated disc, it is necessary to remove some of the plates.
Today, surgery dominates minimally invasive techniques, requiring only a small incision in the lower back. Proponents of this method claim that it is safe. They also believe that the procedure prevents scarring around the nerves and joints and helps patients recover more quickly.
Join
It is an intervention that joins two or more bones in one, avoiding the wear and tear of the ends of the bones and joints.
Rehabilitation
The doctor may recommend that the patient see a physical therapist several times a week for 4 to 6 weeks. In some cases, patients need additional help.
The first year of treatment is necessary to control symptoms. The therapist will work with you to find positions and movements that will alleviate the pain. Heat, cold, ultrasound and electrical stimulation can be prescribed to relieve pain and muscle spasm. Massage or specialized forms of soft tissue mobilization can also be used. These procedures help the patient to perform movements with ease.
Usually, adjusting the treatment helps to restore the sensitivity of the spinal muscles and nerves, reducing pain and improving mobility.
The main purpose of therapy is to teach the patient how to manipulate to prevent future problems. The patient will be guided through a series of exercises to improve flexibility. The patient will also receive a strategy to help with recurring symptoms.
Each person must study and consider all types of osteochondrosis to prevent the development of this disease in themselves and in their loved ones. After all, the treatment of destroyed vertebrae is impossible, the therapy aims to relieve pain symptoms and achieve long-term remission. You also need to remember a simple but effective rule:the best cure is prevention. . .
Prevention of osteochondrosis
Prevention is quite simple - it is a healthy diet, regular muscle activity, daily morning warm-up, a healthy and active lifestyle and a monthly visit.osteopathic sessionsfor the correction and removal of musculoskeletal tensions. Following these rules is enough to never face the mentioned problem and avoid terrible symptoms and treatment for life.